Targeted Therapies: Why India is Leading the Way in Novel Drug Delivery Technologies
India is rapidly emerging as a global leader in novel drug delivery technologies due to its large, diverse patient population, skilled researchers, cost-effective infrastructure, and a robust healthcare ecosystem. These factors are propelling India to the forefront of targeted drug delivery systems and clinical research innovations.
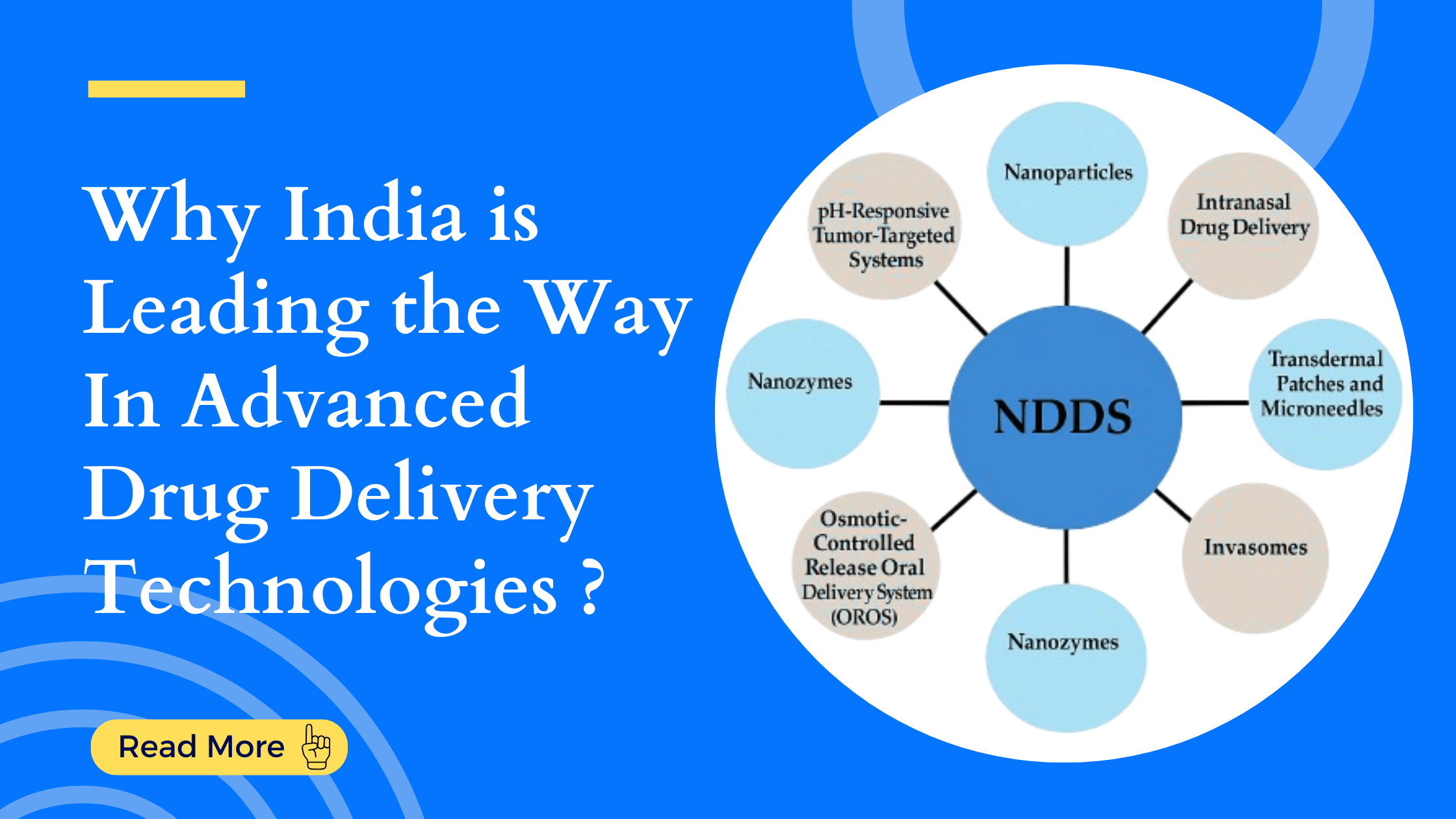
What Are Novel Drug Delivery Technologies (NDDS)?
Novel Drug Delivery Systems (NDDS) are advanced methods developed to deliver drugs in a more efficient, targeted, and controlled way. The main goals of NDDS include:
Enhanced drug targeting to specific tissues or organs
Controlled and sustained drug release
Reduced side effects and toxicity
Improved patient compliance and outcomes
Increased drug bioavailability
NDDS utilizes advanced tools like nanoparticles, liposomes, microneedles, and bioprinting to deliver drugs precisely and safely, transforming the landscape of pharmaceutical development and personalized medicine.
Types of Novel Drug Delivery Technologies
1. Nanoparticles
-
Tiny particles (1–100 nanometers) used to transport drugs directly to disease sites.
-
Made from lipids, polymers, or metals.
-
Offer high absorption and targeted drug release.
2. Nanozymes
-
Synthetic enzyme-like particles made from nanoparticles.
-
Useful in cancer therapy and detoxification by mimicking natural enzymes.
-
Allow for precise, low-toxicity treatments.
3. Intranasal Drug Delivery
-
Administered via nasal sprays, drops, or powders.
-
Enables rapid absorption through nasal blood vessels.
-
Bypasses the digestive system for faster action.
4. Transdermal Patches and Microneedles
-
Deliver drugs through the skin, reducing the need for injections.
-
Non-invasive, painless, and provide sustained release.
-
Ideal for chronic pain, hormone therapy, and vaccines.
5. Invasomes
-
Made from phospholipids, terpenes, and ethanol.
-
Designed to improve drug absorption through the skin.
-
Effective for drugs that don’t penetrate easily.
6. Ultrasound-Triggered Hydrogels
-
Hydrogels release drugs when exposed to ultrasound waves.
-
Useful for site-specific delivery, such as targeting tumors.
-
Reduces side effects by focusing the drug where it’s needed.
7. Magnetic Electrospun Fibers
-
Contain drugs and magnetic nanoparticles within fibers.
-
Drug release is remotely triggered using magnetic fields.
-
Beneficial for oncology, wound care, and pain management.
8. Bioprinting
-
Uses 3D printing with living cells and bio-inks.
-
Creates tissue models for personalized drug testing.
-
Reduces the need for animal testing and improves drug trial accuracy.
9. pH-Responsive Tumor-Targeted Systems
-
Activate only in acidic environments, like tumor sites.
-
Ensure minimal impact on healthy tissues.
-
Improve cancer therapy outcomes.
10. Osmotic-Controlled Release Oral Systems (OROS)
-
Tablet systems that use water-driven pressure for steady drug release.
-
Maintain consistent drug levels in the bloodstream.
-
Improve patient adherence and therapeutic effects.
Traditional Drug Delivery Methods in India: A Look Back
Historically, India’s clinical trials used conventional drug delivery forms such as:
-
Oral Tablets and Capsules – Most common method for systemic effects.
-
Injections – Intravenous or intramuscular for quick results.
-
Topical Creams and Gels – For localized skin treatments.
Challenges with Traditional Methods:
-
Systemic side effects due to poor targeting
-
Low bioavailability and fast drug degradation
-
Frequent dosing required
-
First-pass metabolism reducing drug potency
How NDDS Is Transforming Clinical Trials in India
✅ Benefits of NDDS in Clinical Trials:
-
Improved Targeting: Focuses drug action on specific sites (e.g., tumors).
-
Reduced Side Effects: Lowers systemic exposure and enhances safety.
-
Better Compliance: Controlled release reduces the number of doses needed.
-
Accurate Results: Uniform drug delivery provides consistent trial outcomes.
-
Enables Complex Therapies: Supports delivery of biologics, mRNA, or unstable molecules.
Why India Is Leading the Way in Advanced Drug Delivery
India’s leadership in novel drug delivery technologies is driven by:
Skilled pharmaceutical and biotech talent
Strong CROs like Abiogenesis Clinpharm
Lower trial costs without compromising quality
Access to large patient pools for rapid recruitment
Supportive regulatory frameworks and global partnerships
Abiogenesis Clinpharm: Driving Innovation in Drug Delivery Trials
At Abiogenesis Clinpharm, we are committed to advancing global healthcare by supporting clinical trials that involve targeted therapies and novel drug delivery systems. Our dedicated team works with cutting-edge technologies like nanoparticles, microneedles, and 3D bioprinting to bring more precise, safer, and effective treatments to patients worldwide.
We support sponsors across various therapeutic areas, ensuring regulatory compliance, robust data, and ethical research practices at every phase.
Conclusion
Novel Drug Delivery Technologies are not only improving how medicines are delivered but also how clinical trials are conducted—especially in a forward-thinking hub like India. These innovations are making treatments smarter, safer, and more personalized. As a trusted clinical research organization, Abiogenesis Clinpharm remains at the forefront of this transformation—empowering new possibilities in global drug development.
Let’s work together to redefine what’s possible in clinical research.